How Does Hydrostatic Head Pressure Ensure Borehole Stability?


Contractors drilling foundation shafts will use a can in high water table areas to ensure the proper hydrostatic head. Source: CETCO Drilling Products
Be it vertical rotary mud drilling, horizontal directional drilling or foundation drilling, one commonly overlooked factor in maintaining borehole stability is hydrostatic head pressure. A drilling contractor can have the best drilling fluid or slurry in the world, but if the hydrostatic head pressure is not adequate or is excessive, problems will arise. This article will delve into the effects of hydrostatic head pressure in various drilling applications in order to help drilling contractors use this often overlooked factor to their advantage.
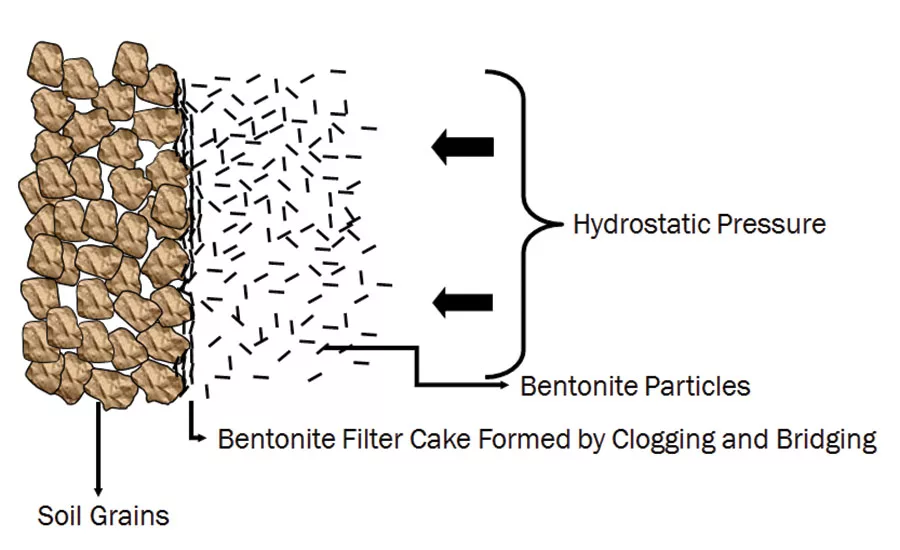
As this author mentioned on a previous article, two things must happen in order to create borehole stability when using a drilling fluid or slurry. The drilling fluid or slurry must create a barrier between the soil and the drilling fluid (filter cake or polymer gel membrane), and we must be able to apply positive pressure against the barrier in order to stabilize the formation. Hydrostatic pressure is providing the positive pressure against the filter cake or polymer gel membrane that keeps the hole stable. Merriam-Webster defines hydrostatic head as “a measure of pressure at a given point in a liquid in terms of the vertical height of a column of the liquid which would produce the same pressure” (Merriam-Webster, 2016). “Groundwater and Wells” (second edition) describes head as “energy contained in a water mass, produced by elevation, pressure, or velocity” (Driscoll, 1995, p.888). To calculate hydrostatic head pressure in pounds per square inch, simply take the weight of the drilling fluid or slurry (in pounds per gallon) times 0.052 times depth.
When drilling foundation drilled shafts, contractors utilizing synthetic slurry (polymer) have a general rule of thumb in that they want a minimum of 6 feet of hydrostatic head above the water table. If the water table is only 4 feet from the surface, for example, then a top can (casing) is set so that they can fill with slurry to get the necessary hydrostatic head pressure.
During drilling operations, contractors must be diligent about topping off the shaft with slurry to provide the necessary hydrostatic head pressure in order to prevent hole-caving. Calculating 6 feet of hydrostatic head pressure above the water table with a synthetic slurry, (8.56 pounds per gallon x 0.052 x 6) theoretically works out to 2.70 pounds of hydrostatic pressure above the water table to maintain borehole stability. Hydrostatic head pressure against the filter cake or polymer gel membrane does not need to be high, it just needs to be positive pressure. In looking at the low positive pressure that is maintaining borehole stability, it is easy to see how pulling out an over-loaded auger bit or a clean-out bucket too quickly can create a vacuum that can cause a shaft to collapse.
Horizontal directional drilling contractors do not have the luxury of setting top cans or casing to provide additional hydrostatic head pressure in situations where the water table is high, therefore they must rely on the fluid-loss/filtration control of the drilling fluids and ensure that the borehole is kept full of fluid. If drilling in unconsolidated soils such as sand and intersecting into an exit pit, the contractor would be wise to maintain a higher fluid level in the return pit to obtain the necessary hydrostatic head pressure in order to stabilize the borehole.
In vertical rotary mud drilling applications, hydrostatic head pressure is even more critical. Oil and gas drilling contractors, for example, will increase the density of the drilling fluid by adding a weighting agent, such as barite, in order to apply enough hydrostatic pressure to prevent high pressure gas from getting to the surface. Water well drilling contractors utilize the same technique in order to drill in areas where flowing aquifers are encountered. The biggest issue this author has seen with hydrostatic head pressure in water well drilling applications is when drilling fluids are high in drill solids and the high density/mud weight leads to loss circulation problems.
An example of this is when this author was working with water well drillers in south Florida who were drilling in sand and mixing high-yield bentonite with hard water, yet not pretreating the water with soda ash. Because of the untreated hard water, high-yield bentonite would not properly yield and perform, and contractors would have to add so much bentonite to stabilize the formation that drill solids would not settle out. Sand contents would rise up to 20 percent and mud weight would climb to around 14.5 pounds per gallon. At a depth of 200 feet, this exerts around 150 psi (14.5 x 0.052 x 200) of hydrostatic head pressure on the formation. A clean drilling fluid (8.6 ppg, with soda ash PAC polymer and a viscosity of around 40 seconds) at the same depth would exert 90 psi on the formation, while providing far superior borehole stability, better penetration rates, fewer loss circulation problems, and less wear and tear on the drill.
As previously mentioned, borehole stability is achieved by a drilling fluid or slurry creating a filter cake or gel membrane to serve as a barrier between the formation and the fluid or slurry. Positive hydrostatic head pressure is needed to apply pressure against the filter cake or polymer gel membrane to maintain borehole stability. The pressure does not need to be great, it just has to be positive pressure.
For more Drilling Fluids columns, visit www.thedriller.com/drillingfluids.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!


